Climate Supportive Livelihoods and Social Inclusion: A Path to a Sustainable Future

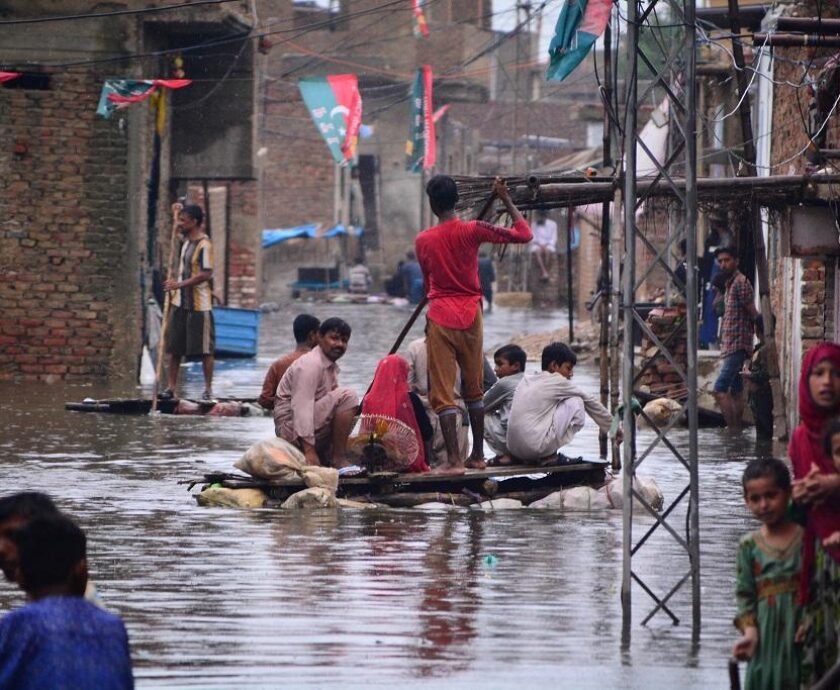
Climate change is a pressing global issue that threatens the livelihoods and well-being of millions of people around the world. The impacts of climate change are already being felt in the form of increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and changes in agricultural yields. These impacts are disproportionately affecting vulnerable communities, particularly those in developing countries.
In the face of these challenges, it is crucial to develop and promote climate supportive livelihoods that are both sustainable and inclusive. Climate supportive livelihoods are those that are resilient to climate change and contribute to the mitigation and adaptation efforts. They also provide equitable access to economic opportunities and social benefits for all.
Key Principles of Climate Supportive Livelihoods
- Sustainability: Climate supportive livelihoods should be based on sustainable practices that conserve natural resources and minimize environmental impact.
-
Resilience: Climate supportive livelihoods should be able to withstand shocks and stresses caused by climate change.
-
Equity: Climate supportive livelihoods should provide equitable access to resources and opportunities for all, regardless of gender, social status, or other factors.
-
Empowerment: Climate supportive livelihoods should empower individuals and communities to take control of their own livelihoods and make informed decisions about their future.
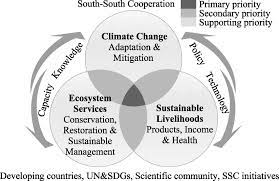
Examples of Climate Supportive Livelihoods
-
Sustainable agriculture: Practices such as agroforestry, organic farming, and conservation agriculture can help farmers adapt to climate change and increase productivity.
-
Renewable energy: Creating jobs in the renewable energy sector can provide economic opportunities while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Ecosystem-based livelihoods: Activities such as ecotourism and sustainable forestry can generate income while protecting biodiversity.
-
Climate-resilient infrastructure: Investing in infrastructure that is resistant to climate change, such as flood-proof housing and drought-resistant crops, can protect livelihoods and reduce vulnerability.
Social Inclusion in Climate Action
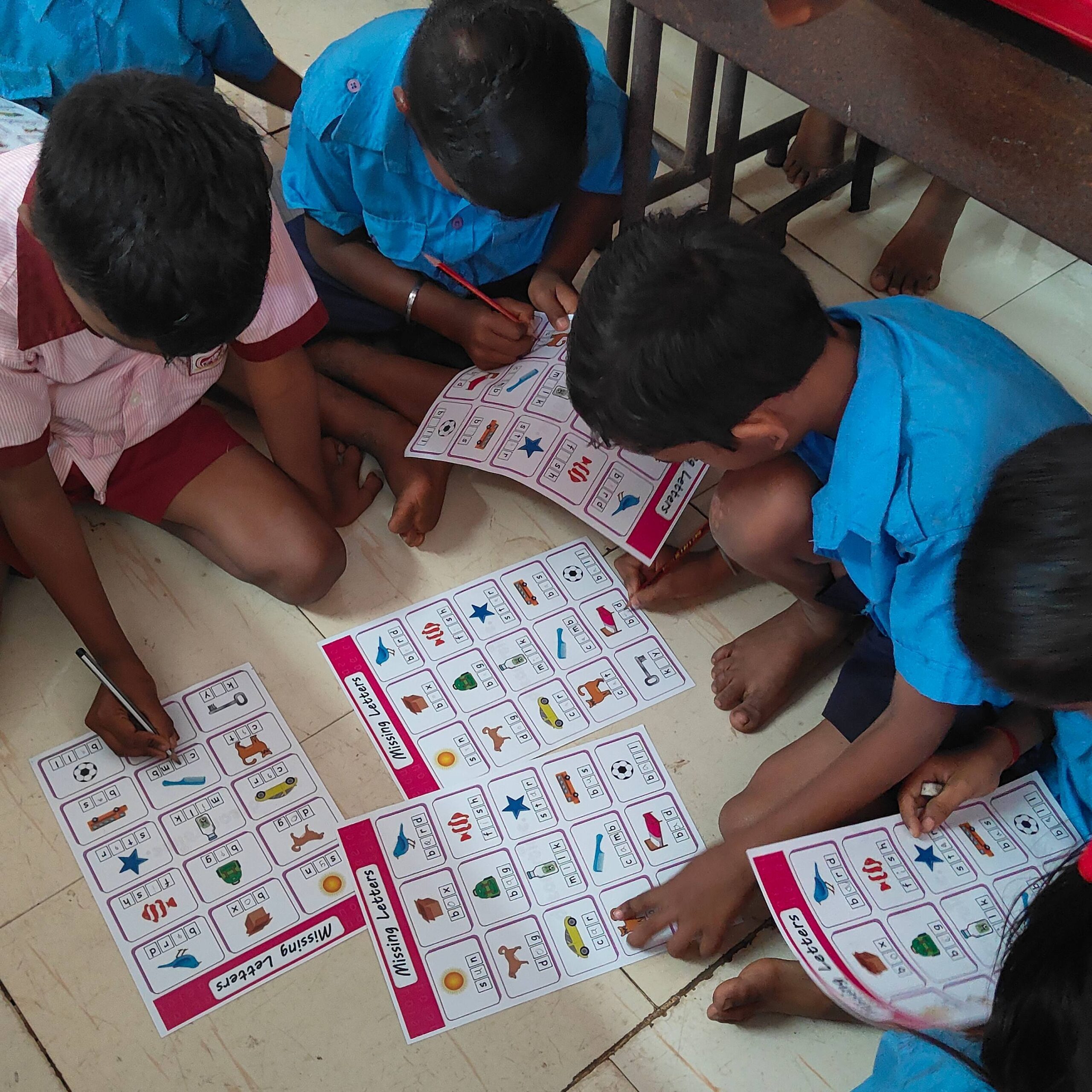
Social inclusion is essential for achieving effective climate action. When all members of society are empowered to participate in decision-making processes and have access to resources and opportunities, they can contribute their unique perspectives and knowledge to climate solutions.
Strategies for Social Inclusion
-
Community engagement: Involve communities in the design and implementation of climate change initiatives to ensure that their needs and priorities are met.
-
Capacity building: Provide training and resources to empower individuals and communities to develop the skills and knowledge they need to adapt to climate change.
-
Gender mainstreaming: Integrate gender considerations into all climate change policies and programs to ensure that women and girls have equal access to resources and opportunities.
-
Indigenous rights: Respect and protect the rights of indigenous peoples, who often have a deep understanding of how to live in harmony with nature.
Conclusion
Climate supportive livelihoods and social inclusion are essential for building a sustainable and equitable future. By investing in sustainable practices, empowering communities, and ensuring that all voices are heard, we can create a world where everyone can thrive in a changing climate.

















